In India, reforms in the regulation of private schools have been argued on the basis of universalizing access to education while recognizing the increasing role of private in enabling that access, particularly for the poor. However, the experience so far has been that the regulations create entry and exit barriers in the provision of education by entrepreneurs thereby reducing competition and keeping the cost of education high. It is in this context that regulation of private education is observed in the case studies to better understand how governments in other parts of the world have managed to harness private investment in education for the benefit of society in general. The study examines three cases of best practices from around the world:
Regulation of Hagwon/supplemental education centres in South Korea,
Per-child funding model in the Netherlands, and
Punjab Education Foundation in Pakistan.
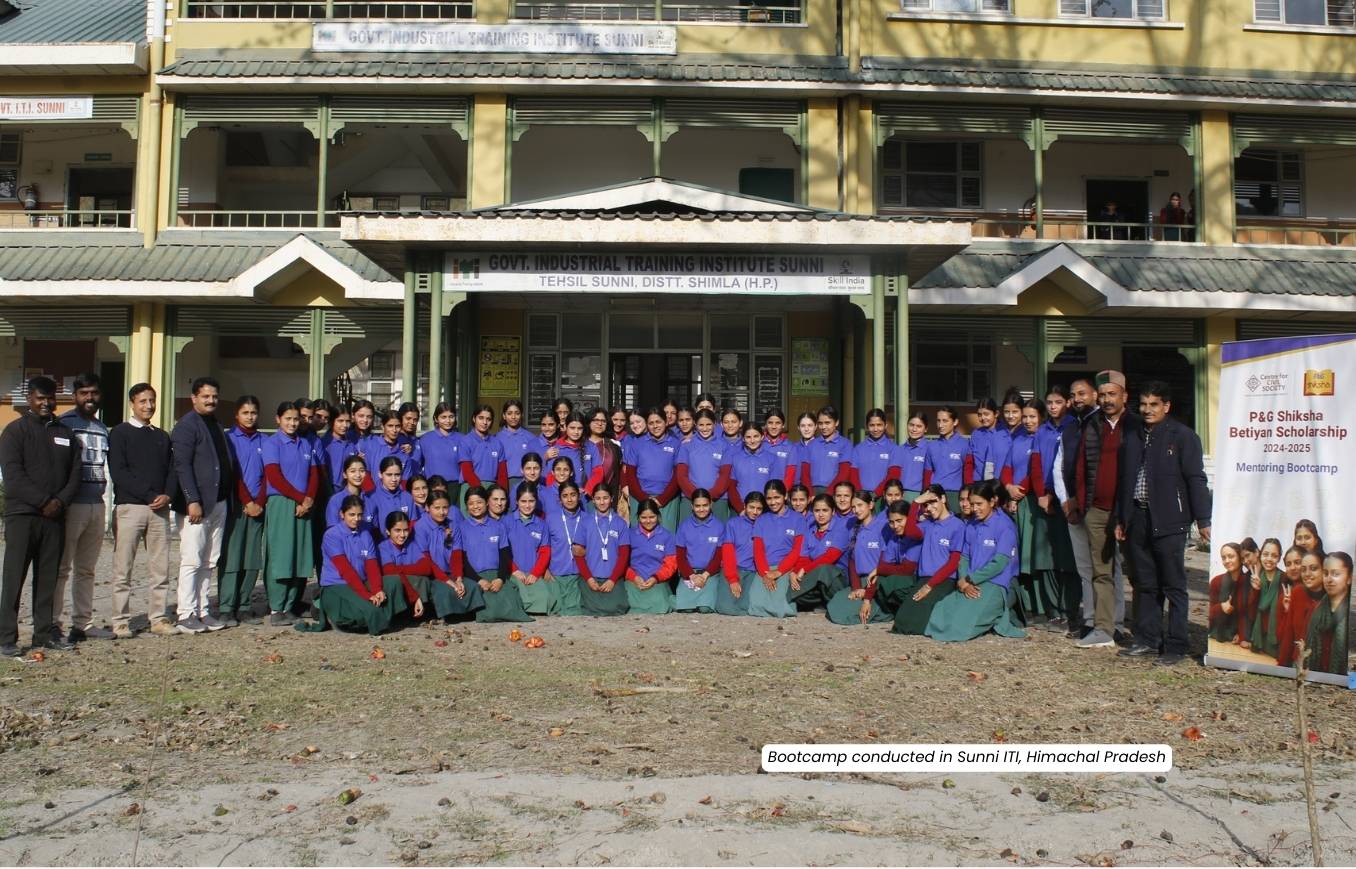

P&G Betiyan Scholarship 2024-25
P&G Betiyan Scholarship Program, launched in collaboration with the Centre for Civil Society in 2021-22, is focused on addressing the gender gap in STEM education (Science, Technology, Engineer